Nuclear Reactions
Radiation
| Property | Alpha Radiation | Beta Radiation | Gamma Radiation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Helium nucleus | High-speed electron | High-energy EM wave |
| Charge | |||
| Mass | |||
| Stopped by | Sheet of paper | Millimetres of aluminium | Centimetres of lead |
| Ionising ability | Strong | Medium | Weak |
| Distance through air | A few centimetres | A few metres | A few kilometres |
Nuclear Binding Energy
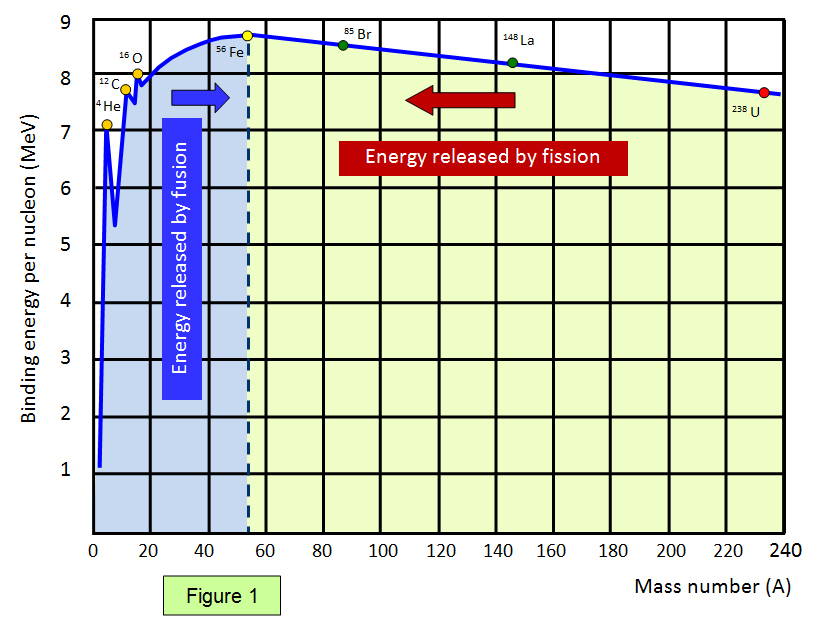
Different atoms have different binding energies per nucleon. If the product of a nuclear reaction has a higher nuclear binding energy than the reactants, energy is released.
Elements with a mass number less than iron can only release energy by fusion, and elements with a mass number greater than iron can only release energy by fission. This is why iron is the heaviest element producible in a star - with heavier elements only achievable during a supernova due to the immense amounts of energy available.