Doppler Effect
Definition
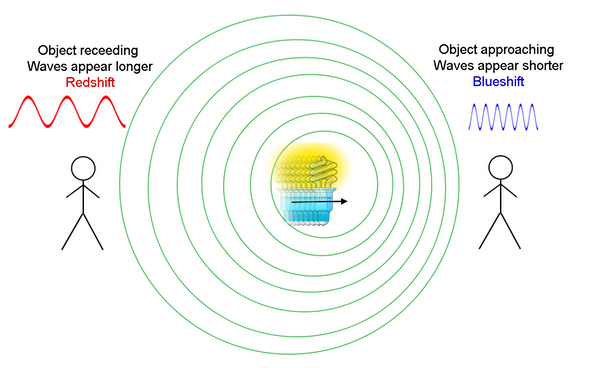
When an observer is travelling towards the source of a wave or vice versa, the wavelength contracts. Since the wave is travelling at a constant velocity, the frequency of the wave therefore increases. If the observer is travelling away from the source, the opposite happens.
Formula
is the frequency observed, in hertz. is the source frequency, in hertz. is the speed of the wave, in metres per second. is the speed of the source, in metres per second.
- If the source is moving towards you,
is subtracted. - If the source is moving away from you,
is added.
To put it another way, the fraction is a ratio of the speed of the wave against the total speed travelling away from you.
Redshift
When atoms of an element are excited, electrons jump up energy levels to outer shells. It then drops back down to its original position, emitting photons of light in the process. Each element has its own distinct emission spectrum, emitting different bands of frequencies.
If the spectra from distant galaxies are analysed and there is a change in the wavelength then the speed of the galaxy relative to us can be calculated. If the wavelength is elongated then it is redshifted and the source is travelling away from us. If the wavelength is contracted then it is blueshifted (equivalent to a negative redshift) and the source is travelling towards us. The greater the redshift or blueshift, the faster the source is moving towards or away from us.
Formulae
is the redshift, with no units! is the recessional velocity, in metres per second. is the speed of light constant, in metres per second. is the observed wavelength of a wave, in any consistent unit of length. is the wavelength of an equivalent wave at rest, in any consistent unit of length.